Heel Pain/Plantar Fasciitis
Heel Pain/Plantar Fasciitis
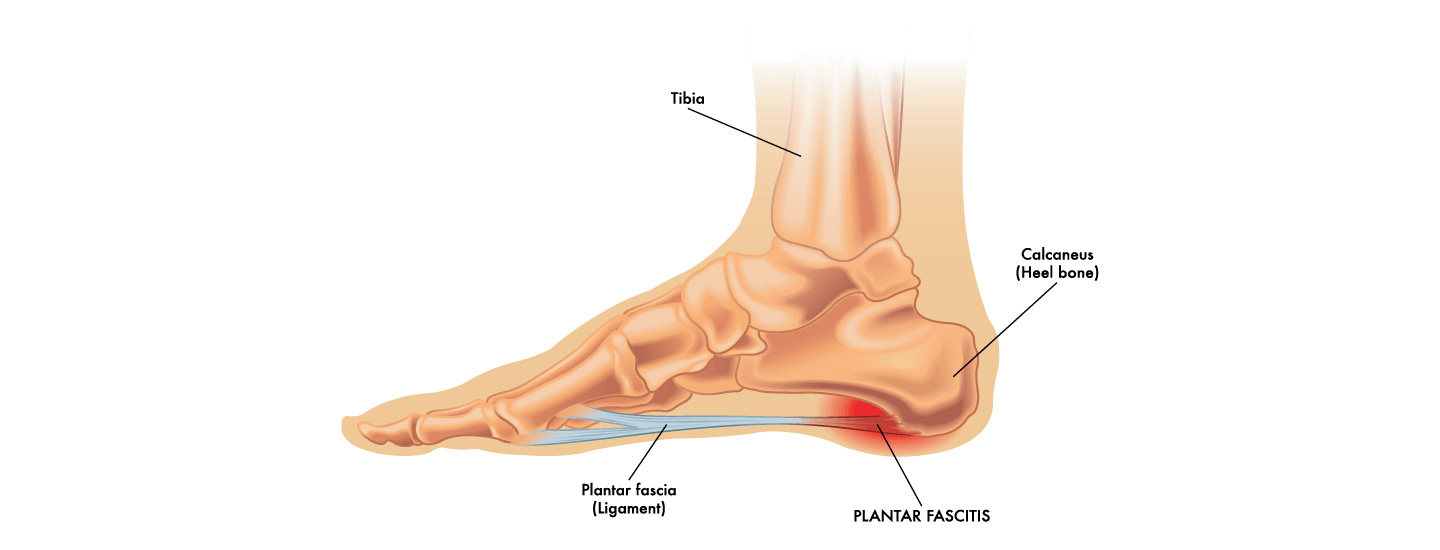
Heel Pain (Plantar Fasciitis/Heel Spur Syndrome)
The plantar fascia is a broad band of connective tissue located along the bottom surface of the foot that runs from the heel bone (calcaneus) to the forefoot (metatarsals). Plantar fasciitis is a common clinical condition caused by overuse or injury of the plantar fascia and is defined as traction degeneration of the
plantar fascial band at its origin on the medial tubercle of the calcaneus. Inflammation, fibrosis, and decreased vascularisation of the fascia occur, causing symptoms of heel pain. The plantar fascia acts as a rubber band to absorb shock as you walk or stand and constantly elongates and contracts. This constant stretching can result in a tear in the soft tissue, most commonly at the heel. Other symptoms that may occur include burning in the sole of the foot, recurring foot pain that is especially aching in the morning or after sitting, or heel pain after beginning a new exercise routine.
Symptoms involve two areas; the arch, and more commonly, the inside heel area. Severe pain can be present, especially in the morning on arising. Common symptoms of plantar fasciitis include:
- Pain in the morning when you first get out of bed
- Pain and stiffness when you start to walk after sitting for a while
- Increasing pain in your heel or arch towards the end of the day
Heel and arch pain is usually the result of abnormal biomechanics that place too much stress on the heel bone and the soft tissues that attach to it. This increased stress causes local inflammation and pain.
The most common cause of this increased stress is excessive pronation, which means that your feet roll inward too much when you walk. As they roll inward the arch of the foot flattens and the arch lengthens. When the arch lengthens there is increased tension on the plantar fascia. However, this condition can also occur in people with high arched feet also.
At Revesby Podiatry we can help:
- Strapping techniques
- Stretching and Strengthening muscles
- Loading and strengthening Exercises
- Footwear Advice
- Biomechanical Assessment and use of orthotics
